Building Intelligent Multi-Agent Systems with LangChain
- saurabhkamal14
- Jan 21
- 4 min read
Have you ever wondered how modern AI applications can handle multiple specialized tasks efficiently? Whether it's customer support, sales analytics, or academic scheduling, today's applications need different AI agents for different problems. That's where LangChain comes in.
LangChain is a framework that allows developers to build sophisticated applications with Large Language Models (LLMs) by creating agents that can intelligently use tools, access databases, and make decisions. Instead of building one monolithic AI system, you can create specialized agents that work together like a well-organized team.
In this guide, I'll walk you through building a real-world multi-agent system for an educational platform using LangChain. You'll learn how to create agents that handle schedules, support tickets, and sales analytics—all working together seamlessly.
What is LangChain?
LangChain is an open-source framework for developing applications powered by language models. It provides tools to:
Connect LLMs to external data sources (databases, APIs, files)
Create agents that can use multiple tools intelligently
Build multi-step reasoning chains for complex tasks
Manage prompts and templates for consistent AI behavior
Think of LangChain as a toolkit that helps you turn a general-purpose AI model into a specialized expert for your specific use case.
Why Do You Need LangChain?
Without LangChain, integrating an LLM with databases and tools would be complex:
You'd manually handle API calls to the LLM
You'd write custom code to parse responses and decide which tool to use
Managing prompts and context would become messy
LangChain abstracts away this complexity, letting you focus on building the actual features.
The Problem: Building an Educational Platform Assistant
Imagine your are building an online learning platform. Your system needs to handle three different types of user queries:
"When does the Java course start?" → Academic Agent
"I have a payment issue with my course" → Support Agent
"Which courses are most popular?" → Analytics Agent
Without LangChain, you'd need to build a complex routing system, handle each case separatly, and integrate with your database manually. With LangChain, you can create specialized agents that do this automatically.
Architecture: The Multi-Agent System

Why This Architecture?
Separation of Concerns: Each agent has a specific responsibility
Scalability: Easy to add new agents (Instructor Agent, Admin Agent, etc.)
Maintainability: Bug fixes and updates are isolated to specific agents
Specialization: Each agent can be fine-tuned for its domain
The Three Specialist Agents
Academic Agent: The Schedule Expert
Responsibility: Answer questions about course schedules and timings
Tools Available:
get_course_schedule_db(course_name) - Fetches course schedule from the database
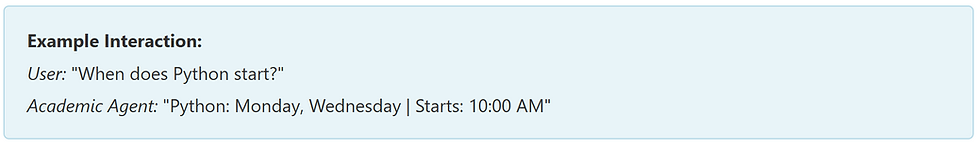
Behind the Scenes: The agent queries the database with:

Support Agent: The Customer Service Team
Responsibility: Handle payment issues, support tickets, and access problems
Tools Available:
get_student_orders(email) - Show student's purchase history and payment status
list_open_tickets(email) - List open support tickets for a student
create_ticket(email, category, description) - Create a new support ticket

Sales/Analytics Agent: The Business Intelligence Team
Responsibility: Provide insights about course popularity and sales trends
Tools Available:
sales_insights_top_courses() - Show top 5 purchased courses

The Supervisor Agent: The Intelligent Router
The Supervisor Agent doesn't answer questions directly. Instead, it understands the user query and routes it to the right specialist.
How It Works:
User asks: "Tell me about sales"
Supervisor analyzes: "This is a sales/analytics questions"
Supervisor decides: "Calls the Sales Agent"
Supervisor returns: Sales Agent's answer
Key Rules:
Always route to exactly ONE specialist agent
Never answer directly
Always return the specialist's answer
This is the genius of the multi-agent architecture: the supervisor handles the high-level decision making, while specialists handle the domain-specific logic.
The Database: Connecting to Real Data
All agents connect to a PostgreSQL database (Neon) with these tables:
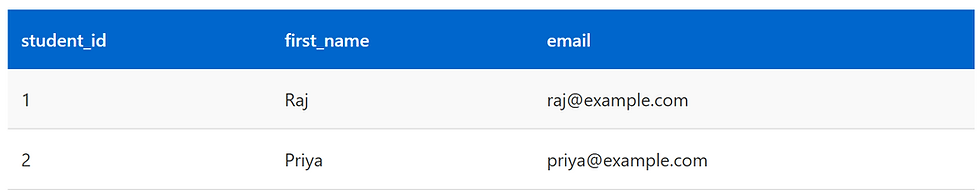
Students Table
Who is taking the courses?
Courses Table
What courses are available?

Orders Table
Who bought what and how much did they pay?

Core LangChain Concepts
Tools
Tools are functions that agents can call to accomplish tasks.

The @tool decorator makes this function available to the AI agent.
Prompts
Prompts define the agent's role and behavior.

This tells the agent exactly what it should do and what tools it can use.
Agents
Agents combine an LLM with tools and a prompt.

The agent now knows:
What LLM to use (Google Gemini)
What tools are available
What its role and constraints are
Agent Executor
The executor runs the agent and handles the tool-calling loop.

The verbose=True setting shows you exactly what the agent is thinking and which tool it's using.
How Data Flows Through the System
Let's trace a complete example:
Example: Customer Asks About Payment

Building the LLM
All agents use the same LLM:

Why Gemini?
Excellent instruction-following
Fast response times
Good at tool usage
Cost-effective
Why Temperature = 0?
temperature = 0: AI always gives the same answer (like 1+1=2)
temperature >= 2: AI varies answers more (creative but inconsistent)
For a database assistant, we want consistency!
Conclusion
LangChain makes it surprisingly easy to build sophisticated multi-agent systems. Instead of single AI model tyring to do everything, you create a team of specialized agents that each excel at their specific domain.
The pattern I explored - a supervisor routing to specialists - applicable to many domains:
E-commerce platforms (Product Agent, Shipping Agent, Refunds Agent)
Healthcare systems (Appointment Agent, Billing Agent, Medical Records Agent)
Financial services (Account Agent, Loan Agent, Investment Agent)
Customer Support (Technical Support, Billing Support, Sales Support)
Links:





